Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Robust covariance estimation¶
Comparison of robustness of different covariance estimators on a corrupted low-dimensional dataset. See also [1].
# Author: Quentin Barthélemy
#
# License: BSD (3-clause)
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from pyriemann.estimation import Covariances
from pyriemann.utils.viz import plot_cov_ellipse
def plot_cov_estimators(ax, X, estimators):
plot_cov_ellipse(ax, C_ref, edgecolor="C0", label='Reference')
for i, est in enumerate(estimators):
C = Covariances(estimator=est).transform(X[np.newaxis, ...])[0]
plot_cov_ellipse(ax, C, edgecolor=f"C{i+2}", label=est)
ax.legend(loc='upper left')
return ax
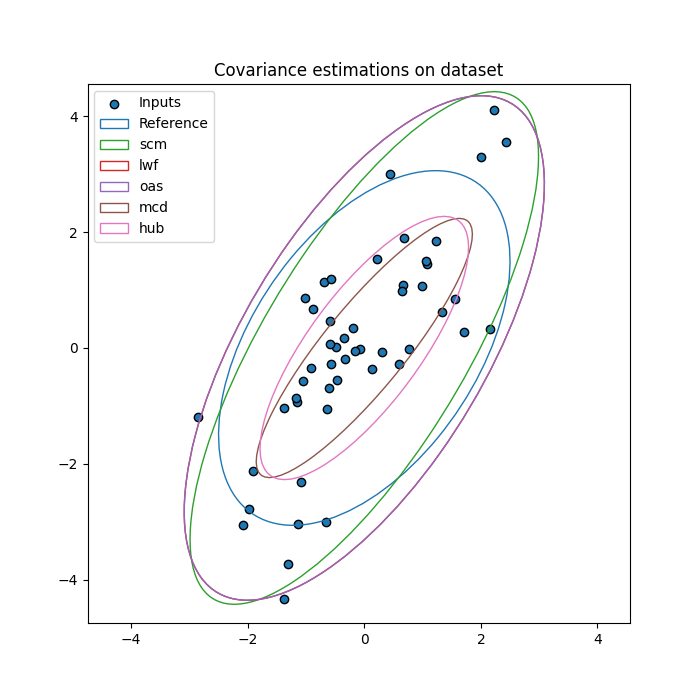
Generate a Gaussian dataset¶
Input samples are generated from a centered 2D Gaussian distribution considered as the reference.
rs = np.random.RandomState(2023)
n_channels, n_inliers = 2, 50
C_ref = np.array([[1, 0.6], [0.6, 1.5]])
X = C_ref @ rs.randn(n_channels, n_inliers)
Estimate covariance matrices on dataset¶
Compare reference covariance matrix to different estimators:
sample covariance matrix (scm),
Ledoit-Wolf shrunk covariance matrix (lwf),
oracle approximating shrunk covariance matrix (oas),
minimum covariance determinant matrix (mcd),
robust Huber’s M-estimator based covariance matrix (hub).
estimators = ["scm", "lwf", "oas", "mcd", "hub"]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 7))
ax.set_title("Covariance estimations on dataset")
ax.scatter(X[0], X[1], c='C0', edgecolors="k", label='Inputs')
ax = plot_cov_estimators(ax, X, estimators)
xlim, ylim = ax.get_xlim(), ax.get_ylim()
min_, max_ = min(xlim[0], ylim[0]), max(xlim[1], ylim[1])
ax.set_xlim(min_, max_)
ax.set_ylim(min_, max_)
plt.show()
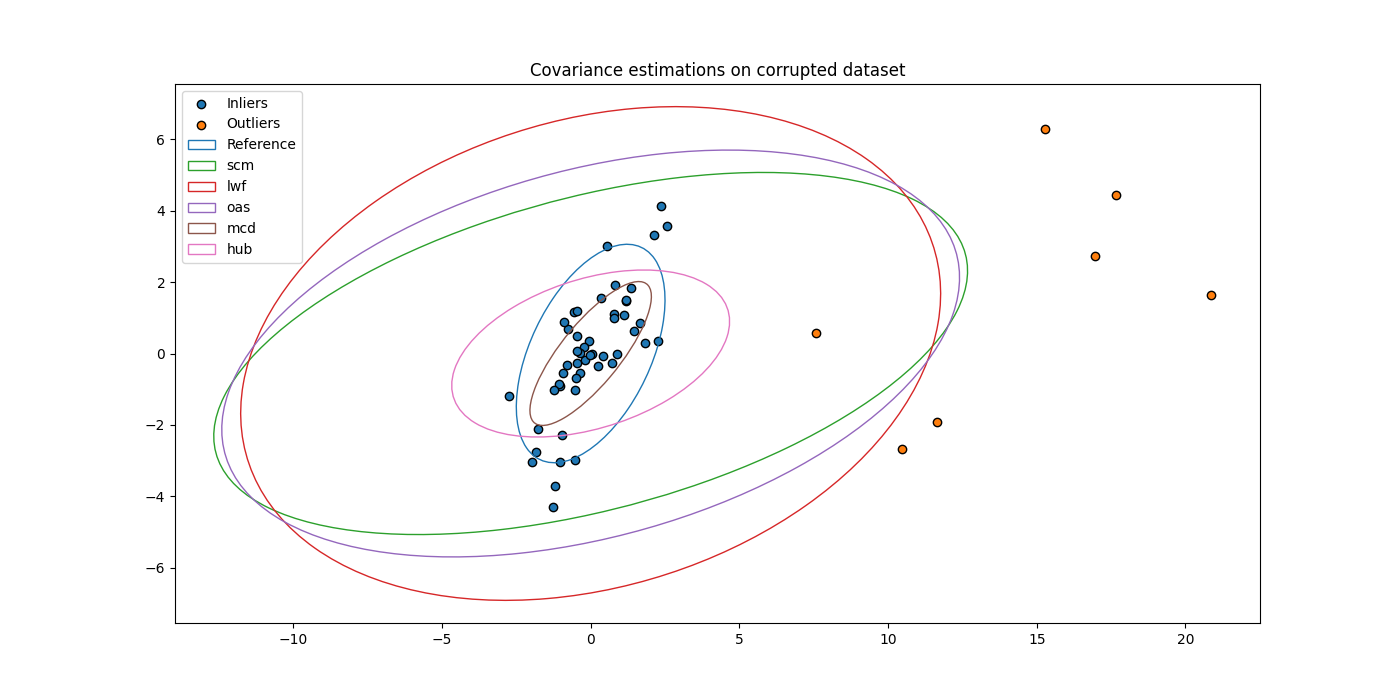
Add outliers to dataset¶
Outliers are added to the dataset.
n_outliers = 7
mu, scale = np.array([15, 1]), 5
Xout = mu[:, np.newaxis] + scale * rs.randn(n_channels, n_outliers)
X = np.concatenate((X, Xout), axis=1)
Estimate covariance matrices on corrupted dataset¶
Compare robustness of the different estimators.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(14, 7))
ax.set_title("Covariance estimations on corrupted dataset")
ax.scatter(X[0, :n_inliers], X[1, :n_inliers], c='C0', edgecolors="k",
label='Inliers')
ax.scatter(X[0, n_inliers:], X[1, n_inliers:], c='C1', edgecolors="k",
label='Outliers')
ax = plot_cov_estimators(ax, X, estimators)
plt.show()
References¶
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.561 seconds)