Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
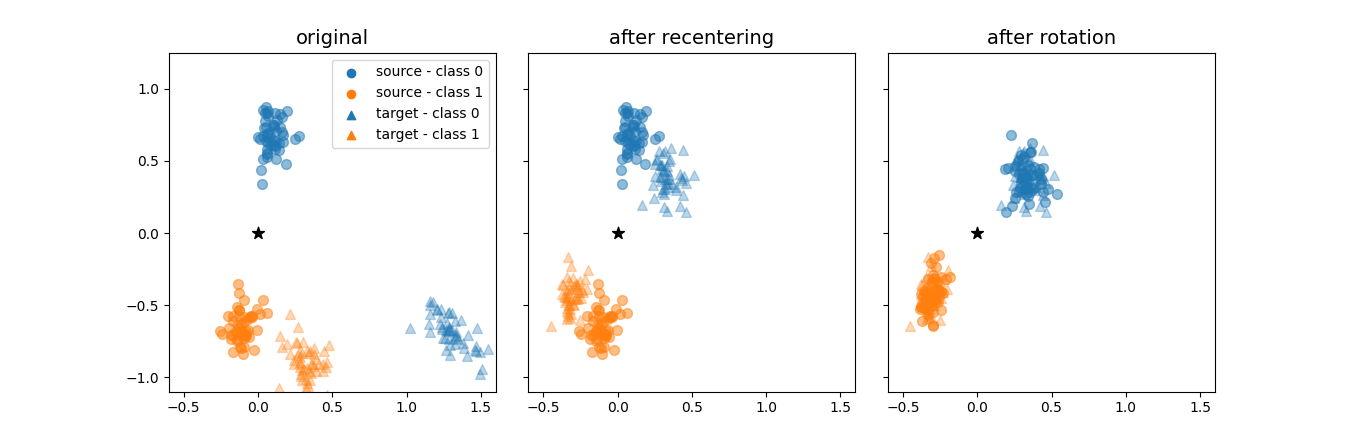
Plot the data transformations in the Riemannian Procrustes Analysis¶
Use the SpectralEmbedding module to plot in 2D the transformations on the data points from source and target domains when applying the Riemannian Procrustes Analysis [1] to match their statistics.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pyriemann.embedding import SpectralEmbedding
from pyriemann.datasets.simulated import make_classification_transfer
from pyriemann.transfer import (
decode_domains,
TLCenter,
TLRotate,
)
Fix seed for reproducible results
seed = 66
# create source and target datasets
n_matrices = 50
X_enc, y_enc = make_classification_transfer(
n_matrices=n_matrices,
class_sep=2.0,
class_disp=0.25,
domain_sep=2.0,
theta=np.pi/4,
random_state=seed
)
# generate dataset
X_org, y, domain = decode_domains(X_enc, y_enc)
# instantiate object for doing spectral embeddings
emb = SpectralEmbedding(n_components=2, metric='riemann')
# create dict to store the embedding after each step of RPA
embedded_points = {}
# embed the original source and target datasets
points = np.concatenate([X_org, np.eye(2)[None, :, :]]) # stack the identity
embedded_points['origin'] = emb.fit_transform(points)
# embed the source and target datasets after recentering
rct = TLCenter(target_domain='target_domain')
X_rct = rct.fit_transform(X_org, y_enc)
points = np.concatenate([X_rct, np.eye(2)[None, :, :]]) # stack the identity
embedded_points['rct'] = emb.fit_transform(points)
# embed the source and target datasets after recentering
rot = TLRotate(target_domain='target_domain', metric='riemann')
X_rot = rot.fit_transform(X_rct, y_enc)
points = np.concatenate([X_org, X_rct, X_rot, np.eye(2)[None, :, :]])
S = emb.fit_transform(points)
S = S - S[-1]
embedded_points['origin'] = S[:4*n_matrices]
embedded_points['rct'] = S[4*n_matrices:8*n_matrices]
embedded_points['rot'] = S[8*n_matrices:-1]
Plot the results, reproducing the Figure 1 of [1].
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(13.5, 4.4), ncols=3, sharey=True)
plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.10)
steps = ['origin', 'rct', 'rot']
titles = ['original', 'after recentering', 'after rotation']
for axi, step, title in zip(ax, steps, titles):
S_step = embedded_points[step]
S_source = S_step[domain == 'source_domain']
y_source = y[domain == 'source_domain']
S_target = S_step[domain == 'target_domain']
y_target = y[domain == 'target_domain']
axi.scatter(
S_source[y_source == '1'][:, 0],
S_source[y_source == '1'][:, 1],
c='C0', s=50, alpha=0.50)
axi.scatter(
S_source[y_source == '2'][:, 0],
S_source[y_source == '2'][:, 1],
c='C1', s=50, alpha=0.50)
axi.scatter(
S_target[y_target == '1'][:, 0],
S_target[y_target == '1'][:, 1],
c='C0', s=50, alpha=0.30, marker="^")
axi.scatter(
S_target[y_target == '2'][:, 0],
S_target[y_target == '2'][:, 1],
c='C1', s=50, alpha=0.30, marker="^")
axi.scatter(S[-1, 0], S[-1, 1], c='k', s=80, marker="*")
axi.set_xlim(-0.60, +1.60)
axi.set_ylim(-1.10, +1.25)
axi.set_xticks([-0.5, 0.0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5])
axi.set_yticks([-1.0, -0.5, 0.0, 0.5, 1.0])
axi.set_title(title, fontsize=14)
ax[0].scatter([], [], c="C0", label="source - class 0")
ax[0].scatter([], [], c="C1", label="source - class 1")
ax[0].scatter([], [], marker="^", c="C0", label="target - class 0")
ax[0].scatter([], [], marker="^", c="C1", label="target - class 1")
ax[0].legend(loc="upper right")
plt.show()
References¶
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.260 seconds)